Scope
1.Scope란?
Scope 종류
-
page
-
페이지 내부의 지역변수 처럼 사용
-
서블릿,JSP 관계없이 선언한 그 페이지 내부에서만 사용
-
-
request
-
http요청을 WAS가 받아서 웹 브라우저에게 응답할 때 까지 유지되는 경우 사용
-
클라이언트로부터 요청이 들어와서 서버가 어떤 일들을 수행한 다음에 응답을 보낼 때 까지 계속 사용가능한 Scope
-
servlet1에서 servlet2파일로 포워딩 시키는 경우 request영역은 같다. 하지만 page영역은 다르다
-
-
session
-
웹 브라우저 별로 변수가 관리되는 경우 사용
-
세션객체가 생성되어 소멸될 때까지 즉, 요청이 하나가 아니라 여러 개의 요청이 들어와도 계속 남아있을 수 있다.
-
상태유지 사용할때 관련이 있다
-
-
application
- 웹 어플리케이션이 시작되고 종료될 때 까지 변수가 유지되는 경우 사용
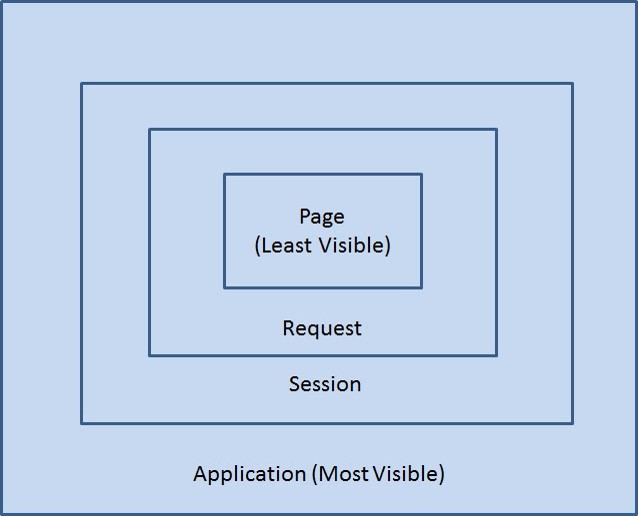
출처 http://inheritingjava.blogspot.kr/2011/04/chapter-42-scope-of-javabeans-in-jsp.html
2. Page Scope
-
PageContext라는 추상클래스를 사용한다.
-
JSP 페이지에서는 pageContext라는 내장 객체를 사용하면 된다. 따로 객체생성할 필요가 없다.
ex)pageContext.setAttribute, pageContext.getAttribute
-
포워드가 될때 Page Scope에 지정된 변수는 사용할 수 없다.
-
사용법은 다른 Scope들과 동일
-
지역변수처럼 사용된다는 것이 다른 Scope들과의 차이점
-
jsp에서 pageScope에 값을 저장 한 후 해당 값을 EL표기법등에서 사용할 때 사용된다.
-
지역 변수처럼 해당 jsp,서블릿 이 실행되는 동안에만 정보를 유지하고자 할 떄 사용된다.
3. Request Scope
- Http 요청을 WAS가 받아 웹 브라우저에게 응답할 때까지 변수 값을 유지하고자 할 경우 사용한다.
- HttpServletRequest 객체를 사용한다.
- JSP에서는 request 내장 변수를 사용한다. 따로 객체생성할 필요가 없다.
- 서블릿에서는 HttpServletRequest 객체를 사용한다.
- 값을 저장할 때는 request객체의 setAttribute() 메소드를 사용한다.
- 값을 읽어 들일 때는 request객체의 getAttribute() 메소드를 사용한다.
- forward 시 값을 유지하고자 사용한다.
4. Session Scope
- 세션은 클라이언트마다 각각 관리해주는 객체다.
- 웹 브라우저 별로 변수를 관리하고자 할 경우 사용한다.
- 웹 브라우저간의 탭 간에는 세션정보가 공유되기 때문에, 각각의 탭에서는 같은 세션정보를 사용할 수 있다.
- HttpSession 인터페이스를 구현한 객체를 사용한다.
- JSP에서는 session 내장 변수를 사용한다. 따로 객체생성할 필요가 없다.
- 서블릿에서는 HttpServletRequest의 getSession()메소드를 이용하여 session 객체를 얻는다.
- 값을 저장할 때는 session 객체의 setAttribute() 메소드를 사용한다.
- 값을 읽어 들일 때는 session 객체의 getAttribute()메소드를 사용한다.
- 장바구니처럼 사용자별로 유지가 되어여할 정보가 있을 때 사용한다.
5. Application Scope
- 이클립스에서 만드는 Dynamic Web Project 하나가 하나의 웹 Application이다. 이 때의 Web Application 내부에 객체 하나
- 하나의 서버에는 여러개의 Web Application이 존재할 수 있다.
- 웹 어플리케이션이 시작되고 종료될 때까지 변수를 사용할 수 있다.
- ServletContext 인터페이스를 구현한 객체를 사용한다.
- JSP에서는 Application 내장 객체를 사용한다. 따로 객체생성할 필요가 없다.
- 서블릿의 경우 getServletContext()메소드를 이용하여 Application객체를 이용한다.
- 웹 어플리케이션 하나당 하나의 application객체가 사용된다
- 값을 저장할 때는 application객체의 setAttribute()메소드를 사용한다.
- 값을 읽어 들일 때는 application객체의 getAttribute()메소드를 사용한다.
- 하나의 웹 어플리케이션 내부에 모든 클라이언트가 공통으로 사용해야 할 값이 있을 때 사용한다.
Application Scope 객체를 이용한 실습
servlet1 파일에서 int 타입 정수를 servlet2파일로 ApplicationScope을 이용하여 전달 후 1을 더한다 그리고 그 수를 jsp 파일로 부터 전달받은 후 다시 2를 더한다.
ApplicationScope01 (서블릿파일1)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
|
package examples;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
/**
* Servlet implementation class ApplicationScope01
*/
@WebServlet("/ApplicationScope01")
public class ApplicationScope01 extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/**
* @see HttpServlet#HttpServlet()
*/
public ApplicationScope01() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
/**
* @see HttpServlet#doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
*/
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html); charset=UTF-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
ServletContext application = getServletContext(); //Application Scope 객체를 얻어냄
int value = 1;
application.setAttribute("val", value); //value를 객체에 저장
out.println("<h1>value :"+value+"</h1>");
}
}
|
cs |
ApplicationScope02 (서블릿파일2)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
|
package examples;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
/**
* Servlet implementation class ApplicationScope02
*/
@WebServlet("/ApplicationScope02")
public class ApplicationScope02 extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/**
* @see HttpServlet#HttpServlet()
*/
public ApplicationScope02() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
/**
* @see HttpServlet#doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
*/
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
ServletContext application = getServletContext(); //Application 객체 가져옴
try {
int getval = (int)application.getAttribute("val") + 1; // ApplicationScope1.서블릿 파일
application.setAttribute("val", getval);
out.println("<h1> value="+getval+"</h1>");
}catch(NullPointerException e) {
out.print("value의 값이 설정되지 않았습니다.");
}
}
}
|
cs |
jsp 파일
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=EUC-KR"
pageEncoding="EUC-KR"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="EUC-KR">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
try{
//JSP의 경우 이미 내장객체를 가지고 있기 때문에 ServletContext를 얻어내서 사용할 필요가 없다
int value = (int) application.getAttribute("val");
value+=2;
application.setAttribute("val", value);
%>
<h1><%=value %></h1>
<%
}catch(NullPointerException ex){
%>
<h1> 설정된 값이 없습니다.</h1>
<%
}
%>
</body>
</html>
|
cs |
'IT > WEB' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 데이터베이스 개념정리 (mysql) (0) | 2020.05.22 |
|---|---|
| EL(표현 언어) 문법 및 정리 (0) | 2020.05.15 |
| JSP개념 (0) | 2020.05.12 |
| Ajax통신의 이해 (0) | 2020.05.12 |
| Ruby를 활용한 Lotto 번호 예제 (0) | 2020.03.01 |